Early detection of oxygen levels is crucial for preventing organ failure and saving lives. The Opticyte VitalO₂ is the first device to monitor both cellular oxygen and blood oxygen saturation (pulse oximetry) in real time. By combining these technologies, VitalO₂ provides comprehensive data to diagnose, treat, and track patient responses. Our commitment to health equity ensures that every patient, regardless of skin tone, receives accurate and timely care through advanced monitoring.
Introducing the
Opticyte VitalO₂
Delivering Definitive Data
When it Matters Most
Advanced Detection of Oxygen Deficiency for Equitable Patient Care
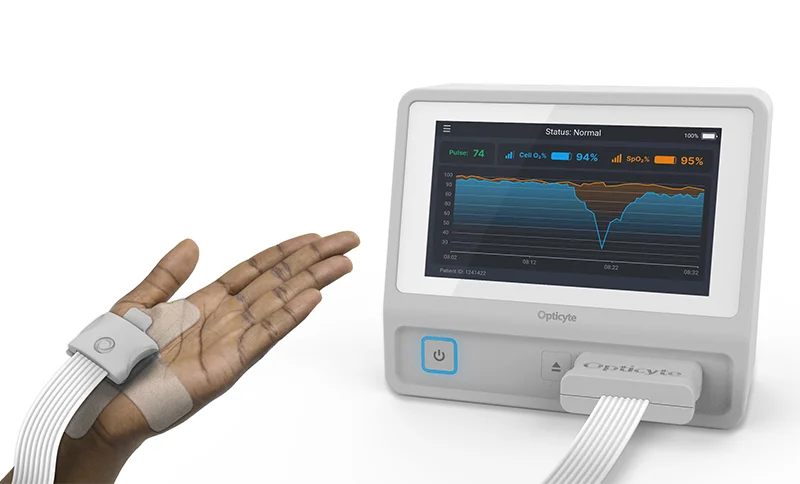
The Opticyte VitalO₂ empowers clinicians with the ability to detect oxygen deficiency both in blood and in organs quickly for earlier intervention. With continuous monitoring, patients will receive personalized precision medicine. This breakthrough, noninvasive technology provides clinicians with an unprecedented, complete picture of a patient’s oxygen levels, from the heart to organ cells, in real time. By allowing them to more quickly narrow in on the source of the health issue and determine precisely when a patient’s oxygen levels are restored, clinicians can make informed, timely decisions that can significantly improve patient outcomes.
Shining Light on the Next Standard of Care
Opticyte’s VitalO₂
One device, Two Essential O₂ Measurements Unbiased by Skin Color
Pulse Ox Technology is Inadequate
The Future of Oximetry:
Better Data for Better Patient Outcomes
Oxygen Supply in Arterial Blood: VitalO₂ monitors pulse oximetry (SpO₂) to evaluate how effectively the lungs oxygenate blood and how efficiently the heart circulates it throughout the body. Oxygen-rich arterial blood is delivered to each vital organ—such as the brain, heart, lungs, kidneys, and skeletal muscles—through its own microcirculatory network of capillaries.
Oxygen Delivery to Cells in Vital Organs: VitalO₂’s Cell O₂ technology offers a powerful window into the body’s oxygen status by measuring how much oxygen reaches skeletal muscle cells as it diffuses out of the microcirculation. Because systemic oxygen deficiencies affect both muscle and vital organs, Cell O₂ reliably indicates cellular oxygenation throughout the body. When oxygen delivery to vital organ cells falls short, organ damage can occur rapidly—but early detection with Cell O₂ will allow clinicians to act sooner to prevent irreversible injury and safeguard organ function. It’s not just monitoring—it’s protection at the cellular level.
VitalO₂ Provides Diagnostic Insight:
The dual measurement capability of Cell O₂ and SpO₂ empowers clinicians to differentiate between problems with microcirculation or blood volume and problems with poor heart or lung function. This leads to more accurate diagnoses and tailored treatments.
Opticyte VitalO₂ Cell O₂ Reading | Opticyte VitalO₂ SpO₂ (Pulse Oximetry) Reading | Medical Condition | What Might Be Causing Low O₂? |
No Oxygen Deficits | |||
Sepsis Hemorrhage, Trauma, Internal Bleeding Anemia | Capillaries are leaky and clogged; vital organs are not receiving adequate O₂ There is not enough circulating blood volume in the body to provide organs with enough O₂ There are not enough red blood cells in circulating blood to provide organs with enough O₂ | ||
COVID-19, Pneumonia Heart Failure | Lungs are not adequately oxygenating blood Heart is unable to adequately pump blood throughout body |
A Beacon to Prevent Organ Failure
VitalO₂ is the World’s First Device to Measure Oxygen in Cells
The Opticyte VitalO₂ shines light in the visible and near-infrared spectrum (500-800 nm) through the skin on the patient’s palm and measures the reflected light. Opticyte’s proprietary pattern-matching algorithm analyzes the optical spectra to produce real-time cellular oxygenation measurements from the patient’s muscle tissue. When there is systemic oxygen deficiency, cells in muscle and core organs like the brain, heart, lungs, kidneys, and liver are deprived of oxygen. Therefore, low oxygen levels in muscle are correlated with low oxygen levels in critical organs and eventual organ failure.
Published Peer-Reviewed Research and Papers
Learn more about Opticyte’s VitalO₂ technology in these published case studies.